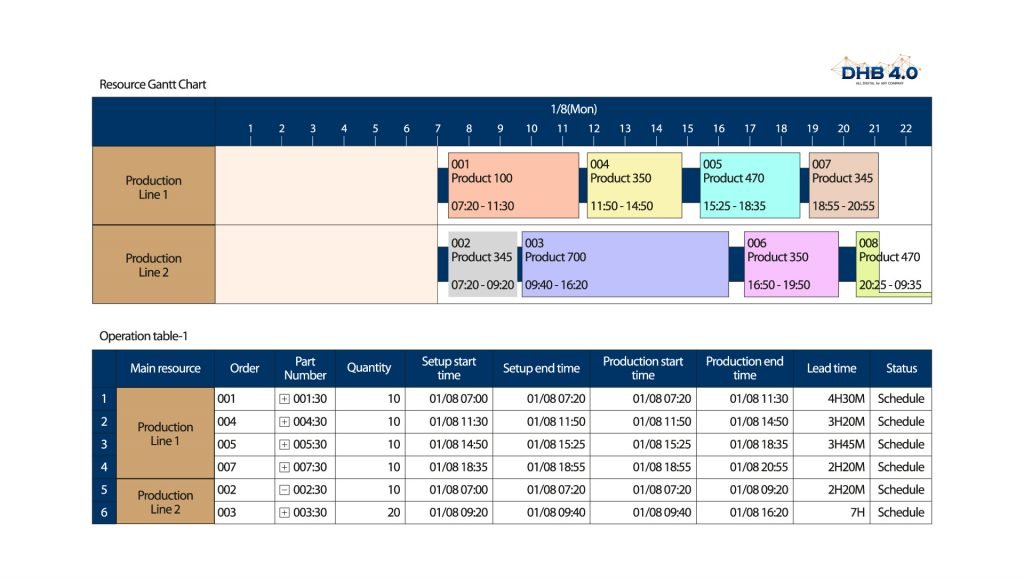
Refinery planning has been among the first applications of mathematical programming in the industry. Advanced and specifics heuristics have been successfully applied to both long-term and short-term refinery planning, but in an isolated way, not with big data, AI, Machine Learning, and other modern solutions.
Fundamentally, DHB4.0 advanced heuristics is about calculating a set of activities under the condition that no activity should be used if a more profitable activity or combination of activities was available. In addition, the method implies values to be placed on scarce resources (marginal costs) which define the opportunities open to the company.
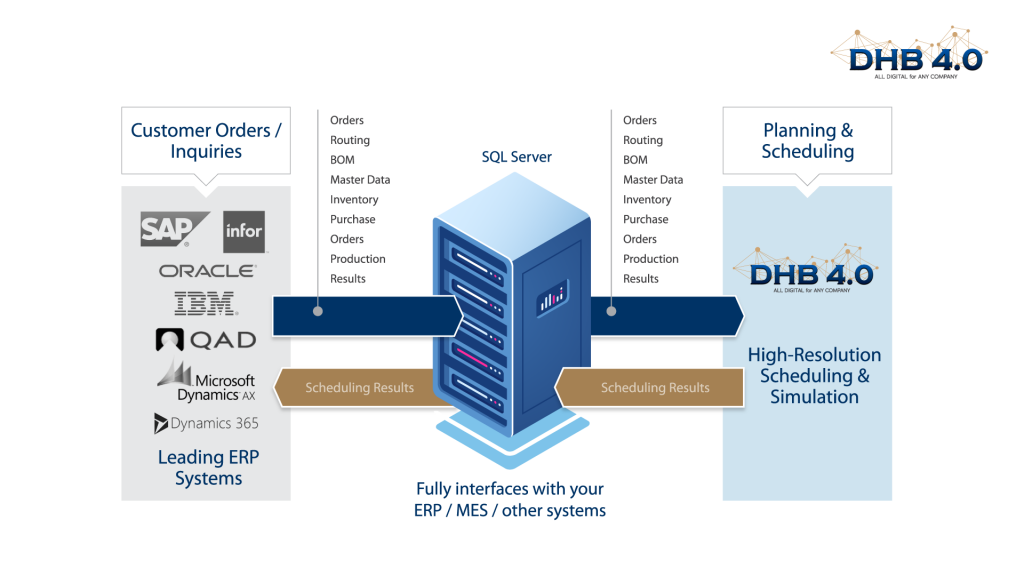
Another important factor that has impacted the way DHB4.0 models were used in recent years has been the arrival of a younger generation of users subject to a higher turnover. In the past, a certain level of expertise in advanced heuristics model building and in-depth interpretation of results was achieved after years of practice. By contrast, today’s users are more interested in a quick overview of a large number of solutions.
Easy to use
Provide a simple and easy to learn modeling environment, data structures, and user interface
Flexible and Scalable
Enable the user to quickly build alternative scenarios through very simple manipulations
Facilitator
Provide summary solutions that can be quickly grasped and compared among each other
Reliable and On-Time
Ensure data consistency between refinery planning and refinery scheduling

North America: +1 (645) 221.6090
Europe: +351 (920) 799.717
LATAM: +55 (19) 9 8251.9536